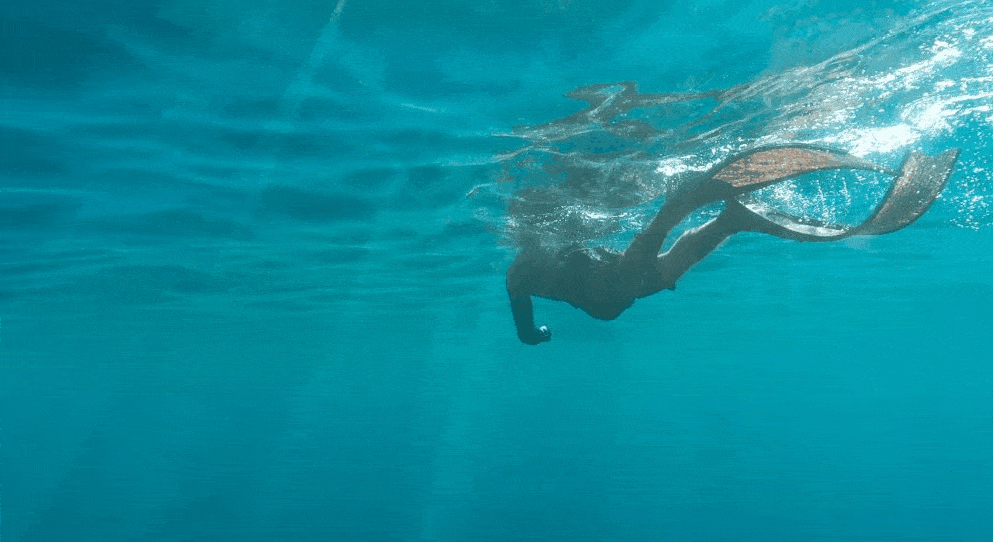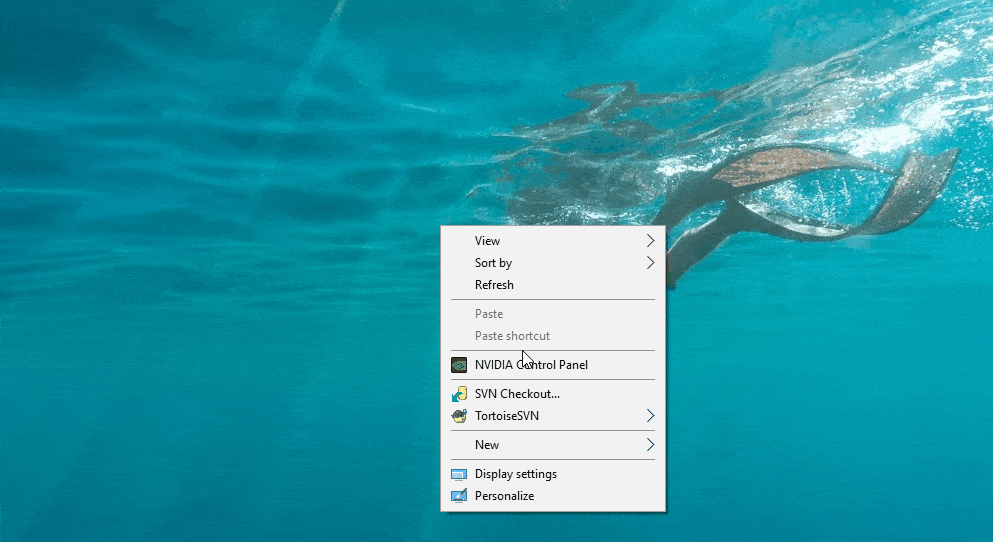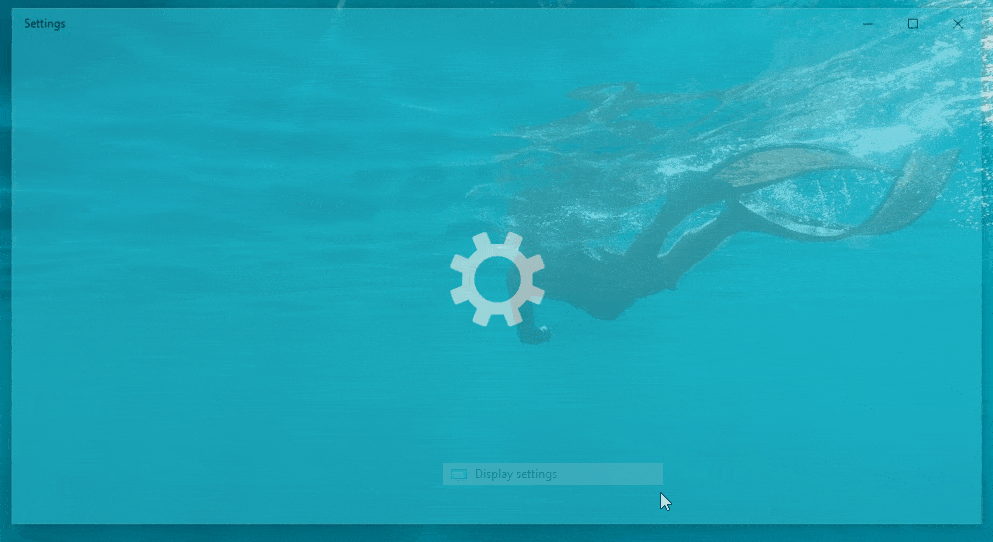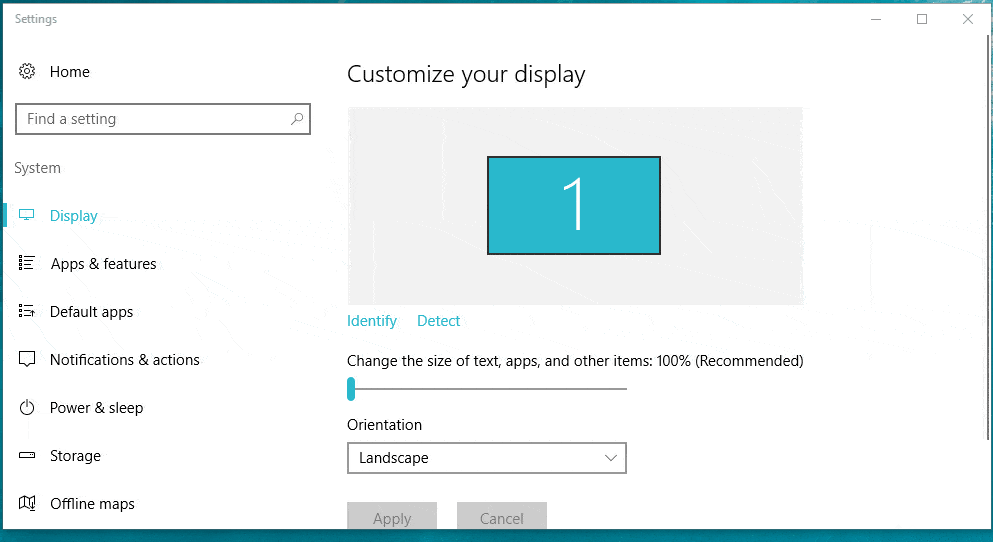Contents
Getting Connected: Monitor Settings
You may have noticed that you can set your monitor or laptop screen to different screen resolutions and to display different numbers of colors. Adjusting these settings can have a significant impact on one how well a web page appears and fits to your screen. To take full advantage of rich content available online, you may need to make some adjustments to your current configuration. Here are some helpful tips.
Screen Resolution
Most people think of resolution in terms of photography or analog television. In those media, resolution indicates picture sharpness. In the computer world, screen resolution refers to the number of the pixels displayed on a screen. Your computer probably came preset to a specific resolution. For instance, if your computer came with a widescreen monitor, it may have chosen a default screen resolution of 1680 × 1050 pixels, meaning the monitor will display a screen that is 1680 pixels wide and 1050 pixels high. This may be the perfect resolution for a 20-inch monitor, but it may not be ideal if you start getting into larger, 24-inch+ monitors.
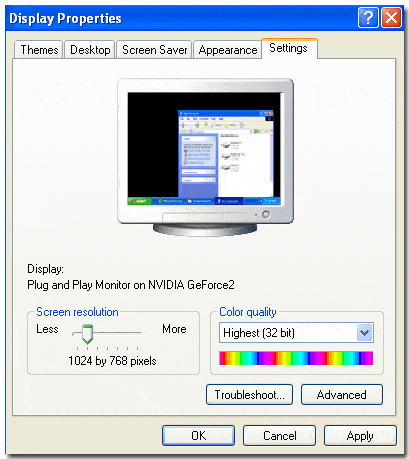
Find the display settings by right-clicking on your homepage:
Screen Sizes
At the same time more and more consumers are switching to small, portable devices to browse the Internet, traditional computers are being designed to support larger and larger monitors. As monitor technologies continue to drop in price, larger monitors are becoming the norm. Ten years ago, a 17-inch monitor was considered huge. Now 20 to 22-inch, widescreen monitors are the norm, but on the small end. Ultra HD monitors are now exceeding 30 inches. The bigger the monitor, the larger the screen resolution you can use, provided your video card supports the larger size.
Types of Monitors
Your options and screen quality will vary considerably depending on the type of monitor your own. Most computers come with a flat-panel LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screen. There are several variations on LCD monitors currently available. TFT-LCD screens, at the lowest end, provide adequate quality and are fairly inexpensive. They are fine for most day-to-day activities such as surfing the Internet and word processing. If you need a crisper display and improved brightness, LED monitors to add LED backlights for improved brightness. For improved viewing angles, consider an IPS-LCD screen. For the highest resolution currently available, 4k UHD monitors provide four times higher resolution than a 1080 HD TV.
Higher quality monitors will not only improve picture quality, clarity, and brightness, but they will allow you to take advantage of higher screen resolutions. If you are considering replacing an older monitor, make sure to research your computer first. While the latest HD monitors can support 3840 x 2160 pixels, your current video card may not be capable of producing that quality.
If you are using an older computer, there’s a chance you still have an older CRT monitor. These are easy to spot since they have a deep back that takes up most of your desk. If you have a CRT monitor, you will be more limited in the number of pixels you can view, and for the higher resolution, you will need to consider purchasing a new monitor. Fortunately, even the most inexpensive option will provide a dramatic difference in picture quality.
Changing the Resolution
Changing your screen resolution is easy, but finding the settings menu will differ depending on your computer:
- For Windows users, from the Start menu, first, select the Control Panel. In the Search Control Panel box at the top right of the window, type “Resolution” and hit Enter. In the search results window, you should see an option for “Adjust screen resolution.” Click on this see the current screen resolution.
- If you are running a Mac computer, click on the Apple icon at the top left of your screen and select System Preferences. Go to the Display tab and click on the Scaled radio button on the right. You should see a list of compatible screen resolutions for your device, which you can select from.
- If you are using a Chromebook, you can change your screen resolution by going to the Settings menu and selecting Display Settings.
Regardless of what type of computer you have, the resolution menu should provide a list of all available screen resolutions, based on your monitor type and video card capabilities. It should also provide a Recommended setting. This is the optimum screen resolution for you monitor–typically the highest resolution your monitor is capable of handling–but that doesn’t mean it is always the best resolution for you. Test out some other options, and see what feels best.
If none of these options look right, make sure you have up-to-date drivers installed for both your monitor and video card. Your operating system can’t pick the best resolution if it doesn’t know what monitor you have or what your video card can handle.
Screen Colors
The number of colors is also important. If you’re a graphic designer or a digital photography aficionado and have a computer loaded with memory, use the Highest setting–32 bit. Otherwise, use the Medium setting–16 bit or 64,000 colors, which gives near the photographic quality and provides a vibrant surfing experience.
Brightness
Most monitors make adjusting the screen brightness as easy as pushing buttons on the top, bottom, or side of the monitor. This is because your brightness needs often change throughout the day, particularly if your office lets in a lot of natural light. On a sunny day, increasing your monitor’s brightness will make it easier to see what’s on your screen. Brighter screens are also better for watching movies, while typing and web browsing may be easier on your eyes with a darker screen. For these same reasons, many laptops include screen brightness controls as alternatives to the F-Keys at the top of your keyboard, and mobile devices usually allow you to adjust the brightness using the notification or action bar, which you can pull down from the top of the screen.
Advanced Settings
Monitors offer a variety of customizable settings, including contrast, color settings, image positioning, and much more. Most monitors come with default settings for these, often consider the optimum settings, but that doesn’t mean they are the best settings for you. Depending on what you are doing with your computer, you may need to adjust these settings manually. Some of these settings can be adjusting using the physical menu keys on your monitor, while others will need to be adjusted using your graphics card’s control panel. If you have installed your graphics card’s software, you can usually find an icon for it in your Windows notification area, at the bottom right of your screen. If you don’t see one, try your control panel or go to your graphics card’s website and make sure you have downloaded the latest version of their software. Once you find the program, play around with each of the setting options until you find the best fit for you. And don’t worry about messing things up. You can always return to the default settings and start over.